Climate Models Overview
CEVE 543 - Fall 2025
2025-10-15
Reflecting on Module 1
Think-pair-share (2 minutes)
What are potential limitations of GEV and nonstationary GEV methods for climate risk assessment?
Key limitations:
- Require long observational records (often unavailable)
- Parametric representation of nonstationarity
- Events with multiple drivers create multimodal distributions
- Model structure uncertainty
In Module 2 we will explore how climate models can mitigate these limitations.
Logistics
Logistics
Climate Risks and Variability
Climate Models Overview
Model Limitations and the Need for Statistical Methods
Problem Set 2
Topics:
- Climate model simulations
- Statistical downscaling
- Bias correction
Focus on practice problems for exam preparation.
Proposed Syllabus Update
Proposal: Remove final exam, redistribute points.
Current
- Problem sets: 10%
- Labs: 10%
- Module tests: 40%
- Final project: 20%
- Final exam: 20%
Proposed
- Problem sets: 15%
- Labs: 15%
- Module tests: 50%
- Final project: 20%
Module 2 Structure
Three-part weekly rhythm:
- Monday - lecture on statistical/computational methods (whiteboard)
- Wednesday - Paper Discussion (slides and class discussion)
- Friday - Virtual lab implementing subset of methods
Module 2 Schedule
| Week | Method | Lab |
|---|---|---|
| Oct 15-27 | Climate data overview | Climate data in Julia |
| Oct 20-24 | Bias Correction | QQ-mapping |
| Oct 27-31 | Weather Typing | PCA + \(K\)-means |
| Nov 3-7 | Hidden Markov models | HMMs |
| Nov 10-14 | Stochastic Weather Generators | TBD |
| Nov 17-21 | Sensitivity Analysis | Exam |
Climate Risks and Variability
Logistics
Climate Risks and Variability
Climate Models Overview
Model Limitations and the Need for Statistical Methods
Climate Risks Cluster
Spatial clustering → portfolio risk. Temporal clustering → insurance/reinsurance viability.
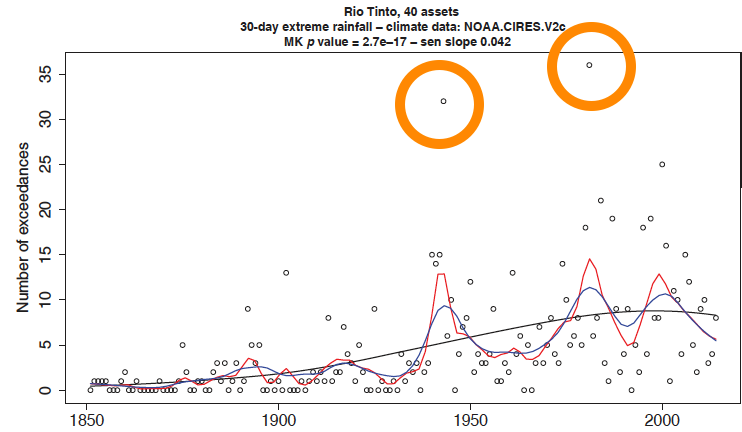
Time series of the yearly number of 30-day extreme rainfall events exceeding the 10-year return level for the Rio Tinto portfolio computed using the 20CR dataset, using 3 windows (11, 21, and 114 years) to illustrate different aspects of long-term variability (Bonnafous, Lall, and Siegel 2017)
Climate Risks Vary on Many Timescales
Multi-timescale variability is essential for design and planning.
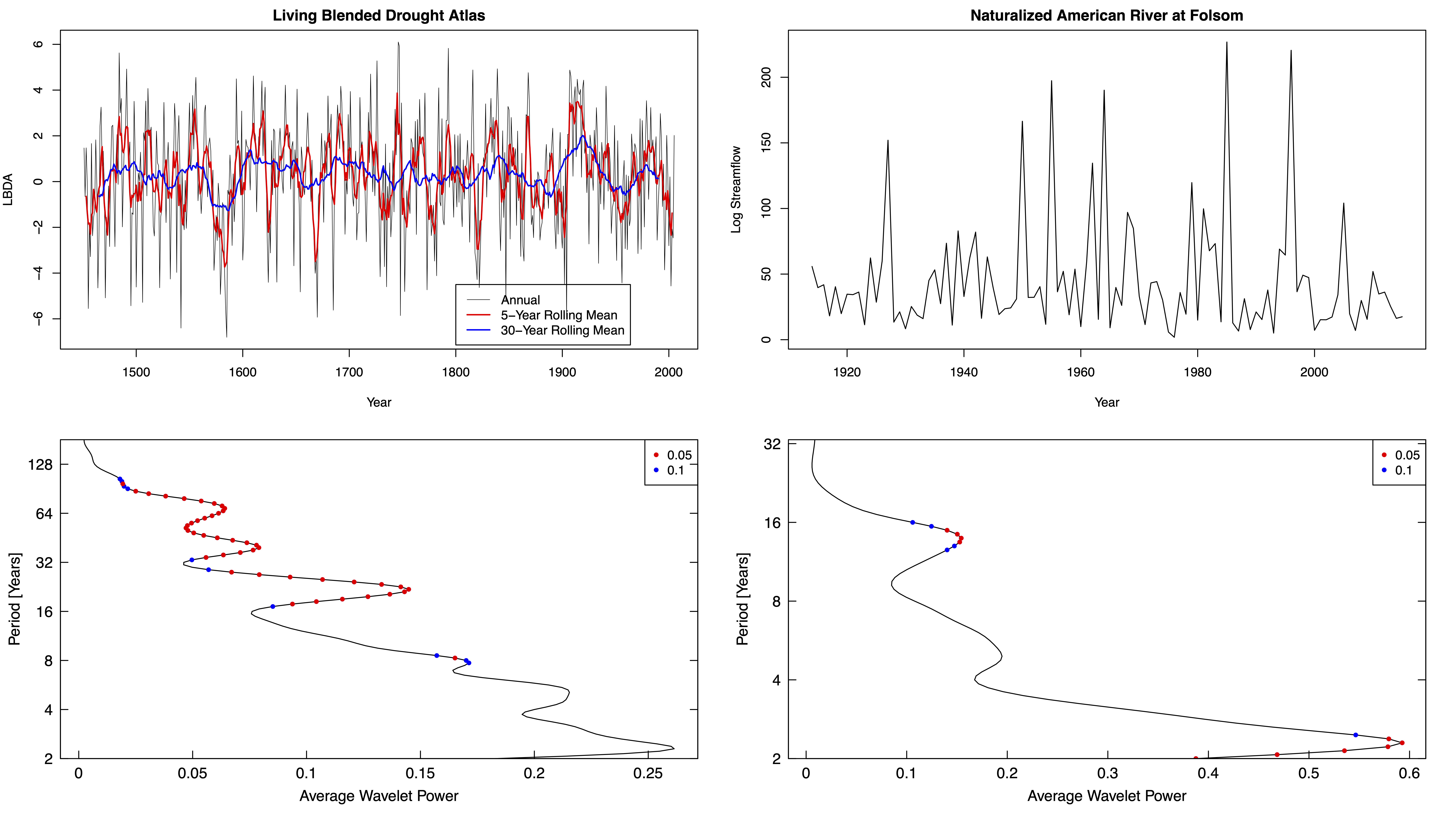
Global wavelet analysis of two (L) living Blended Drought Analysis and (B) Naturalized American River at Folsom (Doss-Gollin et al. 2019)
Nonlinear Dynamics
- Recurrence and persistence of weather patterns (“regimes”) drive many extremes
- Study of low-dimensional chaotic systems provides insight
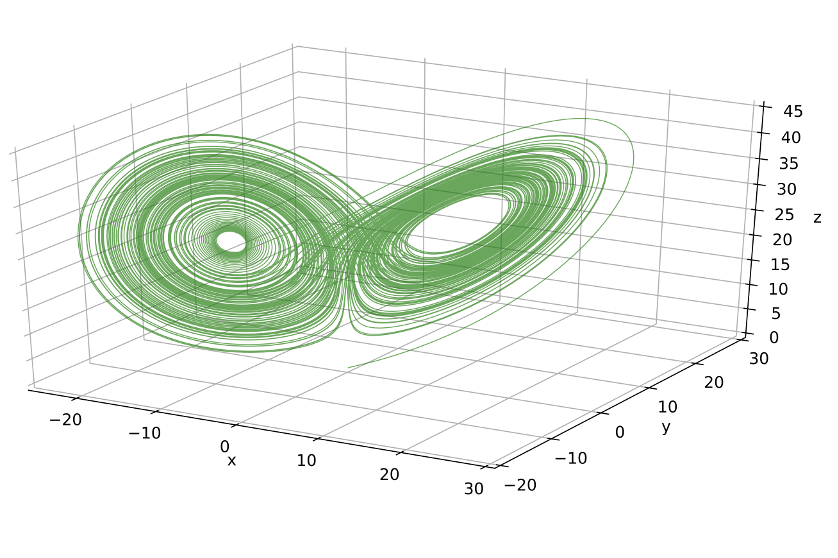
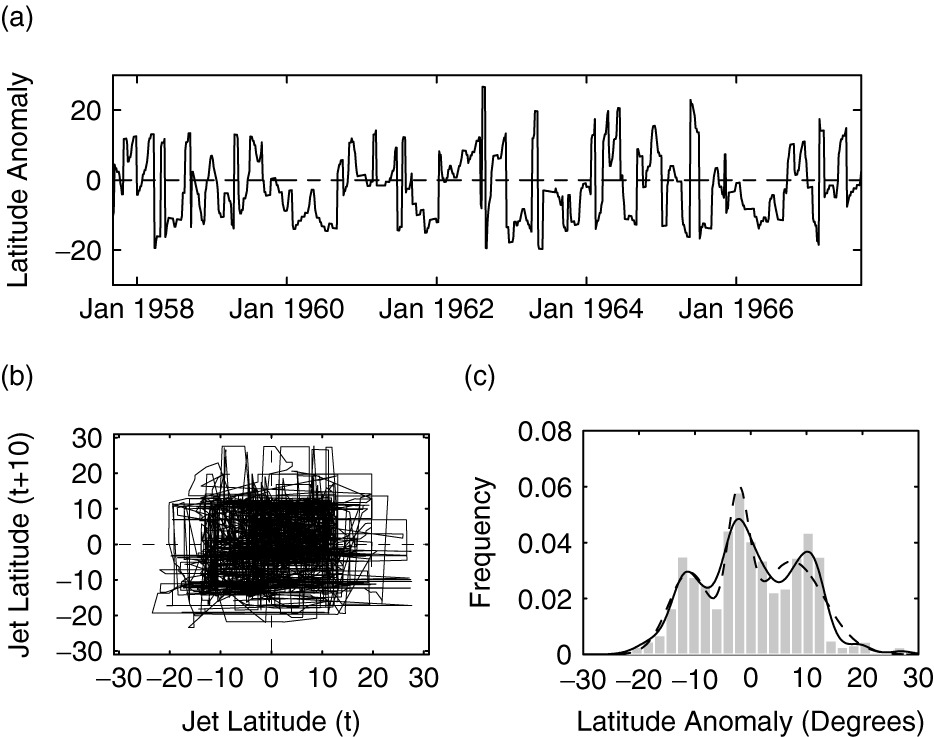
Climate Models Overview
Logistics
Climate Risks and Variability
Climate Models Overview
Model Limitations and the Need for Statistical Methods
What is a Climate Model?

Global grid example (Credit: CliMA)
Numerical solution of PDEs on global grids.
Think-pair-share (1 minute)
What equations do climate models solve?
Weather vs Climate
Weather
- Initial value problem
- Specific atmospheric states
- Days to weeks
- Sensitive to initial conditions
Climate
- Boundary value problem
- Long-term statistics
- Decades to centuries
- Forced by boundary conditions
History
Key milestones (per CarbonBrief):
- 1956: Norman Phillips creates first general circulation model
- 1967: Manabe & Wetherald publish groundbreaking GCM study with doubled CO\(_2\)
- 1979: Charney Report provides critical assessment
- 1988: James Hansen presents climate scenarios to Congress
- 1995: CMIP launched for model intercomparison
Evolution: energy balance models \(\rightarrow\) GCMs \(\rightarrow\) ESMs
Using Climate Model Simulations
Climate models are computationally expensive. We rarely run them ourselves—instead, we use existing simulations.
Coupled Model Intercomparison Project (CMIP): Coordinated effort where modeling centers run standardized experiments.
Key features:
- Common scenarios: All models run same experiments (historical, future emissions pathways)
- Multiple models: Compare structural differences across models
- Ensembles: Multiple realizations per model to quantify internal variability
Discussion
Why coordinate all models to run the same scenarios rather than letting each center choose their own?
CMIP6
Sixth phase (2015-present) addresses three questions:
- How does the Earth system respond to forcing?
- What are the origins and consequences of systematic model biases?
- How can we assess future climate changes given variability and uncertainty?
Scale: 100+ models from ~50 institutions running 23 endorsed experiments.
Experiments include: Historical simulations (1850-2014), future scenarios (SSP1-1.9 through SSP5-8.5), detection & attribution, and specialized experiments.
AI/ML Models
- Weather models: GraphCast, FourCastNet, Pangu-Weather
- Foundation models: Aurora, ClimaX
- Climate emulators: LUCIE, etc.
Discussion
What are the advantages and limitations of AI vs. physics-based models?
Model Limitations and the Need for Statistical Methods
Logistics
Climate Risks and Variability
Climate Models Overview
Model Limitations and the Need for Statistical Methods
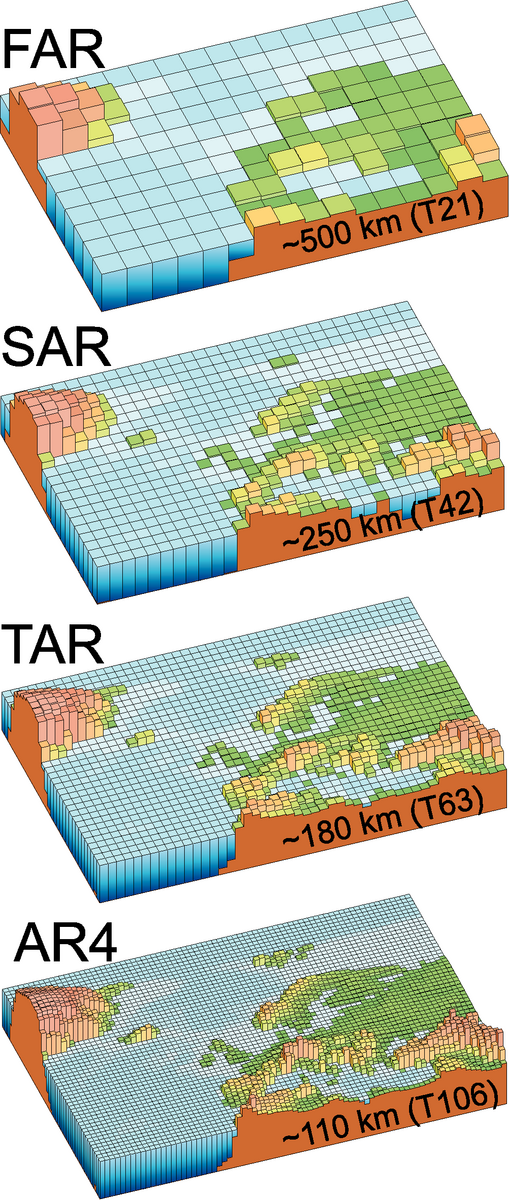
Coarse Resolution
- CMIP6 models don’t resolve tropical cyclones, mesoscale convection, etc.
- Sub-grid processes always require parameterization.
Systematic Biases
Discussion: Model Limitations vs. Value
Think-pair-share (3 minutes)
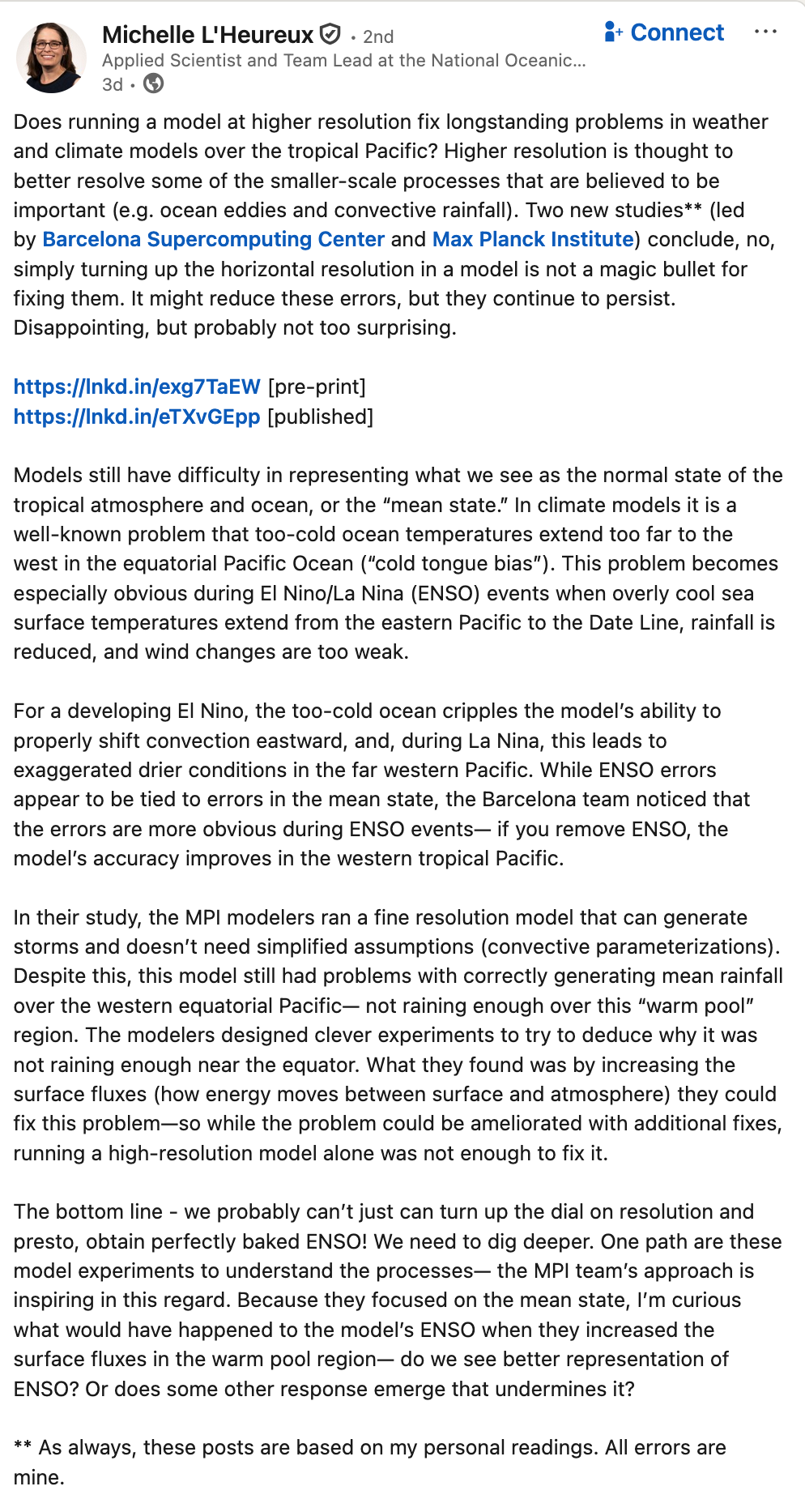
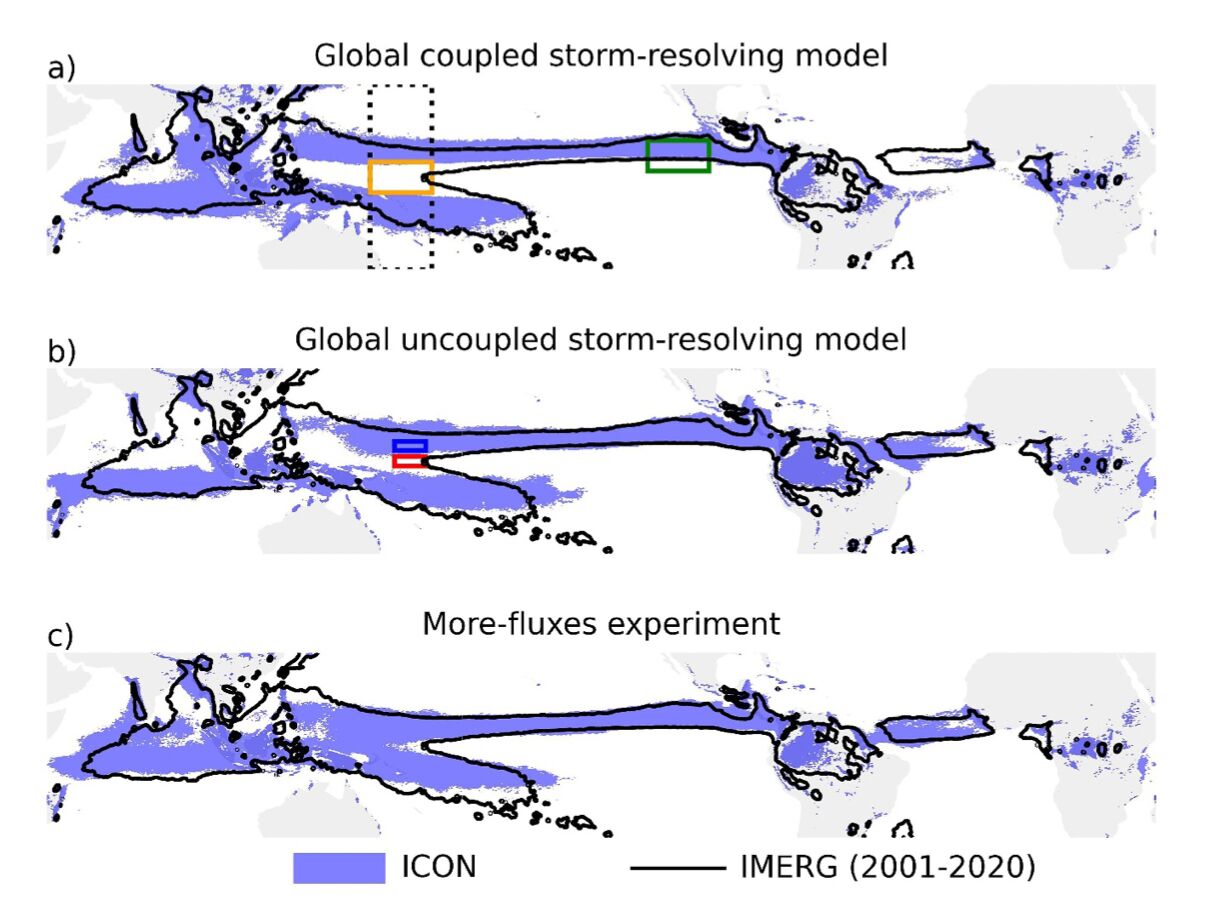
Suppose you are analyzing extreme rainfall in a region where rainfall is strongly modulated by ENSO, but climate models struggle to accurately simulate ENSO dynamics.
Should you use the model simulations for your analysis? What factors would influence your decision?
Key considerations:
- What specific information do you need from the models?
- Can you bias-correct or statistically adjust for ENSO biases?
- Are there alternative approaches (e.g., weather typing, conditional sampling)?
- What are the consequences of getting it wrong?